Physics 121, Midterm Exam #3
Tuesday April 22, 2008
8.00 am – 9.30 am
Do not turn the pages of the exam until
you are instructed to do so.
You are responsible for reading
the following rules carefully before beginning.
Exam rules: You may use only a
writing instrument while taking this test. You may not consult
any calculators, computers, books, nor each other.
Answer the multiple-choice questions (problems 1 – 10) by marking your answer on the scantron form. For each multiple-choice question (problems 1 – 10), select only one answer. Questions with more than one answer selected will be considered incorrect. Problems 11, 12, and 13 must be answered in the blue exam booklets and need to be well motivated and expressed in terms of the variables used in the problem. Answer questions 11 and 12 in booklet # 1 and question 13 in booklet # 2. You will receive partial credit where appropriate, but only when we can read your solution. Answers that are not motivated will not receive any credit, even if correct.
At the end of the exam, you need
to hand in your exam, the blue exam booklets, and your scantron form. All items must be clearly labeled
with your name, your student ID number, and your workshop
day/time. If any of these
items is missing, we will not grade your exam, and you will receive a score of
0 points.
Name: __________________________________________________
ID number:
______________________________________________
Workshop Day/Time: ______________________________________
Intentionally left blank
Problem 1 (2.5 points)
Under what conditions does the
equation ![]() apply for a system of particles?
apply for a system of particles?
1.
Under
all conditions.
2.
Only
if the system consists of a single particle.
3.
Only
if the center of mass of the system is at rest.
4.
If the
quantities are calculated in an inertial reference frame or about the center of
mass.
Problem 2 (2.5 points)
An object is spinning freely about a
fixed axis when a small piece of its surface is ejected. The remainder will continue to spin
with its initial angular velocity if the ejected piece leaves the surface with
a velocity
1.
that is directly away from the axis of rotation.
2.
that is zero.
3.
that is equal to the velocity of the center of mass of the
initial object.
4.
that is equal to its velocity on the surface of the object at
the moment it is ejected.
Problem 3 (2.5 points)
What happens to the precession rate
of a spinning top as the angular velocity of the top about its axis decreases?
1.
The
precession rate remains constant.
2.
The
precession rate decreases.
3.
The
precession rate increases.
4.
It depends on the angle of tilt of the top.
Problem 4 (2.5 points)
The typical behavior of a solid that
has reached its proportional limit is that the strain for a given increase in
stress is
1.
Greater
than before the proportional limit is reached
2.
Less
than before the proportional limit is reached
3.
The
same as before the proportional limit is reached
4.
Unlimited,
as this the point at which the material fractures
Problem 5 (2.5 points)
A pencil standing vertically on its
tip is an example of
1.
Non-equilibrium
2.
Stable
equilibrium
3.
Unstable
equilibrium
4.
Neutral
equilibrium
Problem 6 (2.5 points)
What statement is necessarily true
for a system that has no net torque and no net force acting on it?
1.
The
system is in static equilibrium.
2.
The
system is in stable static equilibrium.
3.
The
system is not in equilibrium.
4.
The
system is not undergoing translational or angular acceleration.
Problem 7 (2.5 points)
The acceleration of gravity at the
surface of the moon is approximately one-sixth the acceleration of gravity at
the surface of the earth. A
pendulum at the surface of the earth has length L. On the surface of the moon, a pendulum with the same period
will have a length
1.
6L
2.
L/6
3.
36L
4.
L/![]()
Problem 8 (2.5 points)
The amplitude of a damped harmonic
oscillator decreases to half its initial amplitude in time t. How much longer does it take for the amplitude to reduce to
one-fourth of its original amplitude?
1.
t/2
2.
t/4
3.
t ln 2
4.
t
Problem 9 (2.5 points)
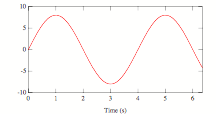
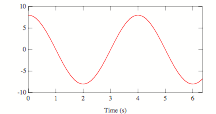
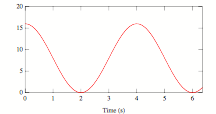
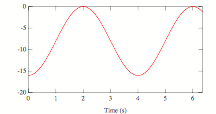
Which of the following graphs could represent the kinetic energy of simple harmonic motion as function of time?
|
A |
B |
|
D |
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Problem 10 (2.5 points)
|
A |
B |
|
C |
D |
|
E |
|
Match the pictures of the ball parks shown above to the team names listed below.
1. Yankees
2. White Sox
3. Mets
4. Cubs
5. Red Sox
ABCDE =
1. 12345
2. 21453
3. 21534
4. 31542
5. 31254
6. 42351
Problem
11 (25 points) Answer
in Exam Booklet 1
Two identical blocks, each of mass M, are connected by a light string over a frictionless pulley of radius R and rotational inertia I (see Figure). The string does not slip on the pulley, and it is not known whether or not there is friction between the plane and the sliding block. When the system is released, it is found that the pulley turns through an angle q in time t and the linear acceleration of the blocks is constant.
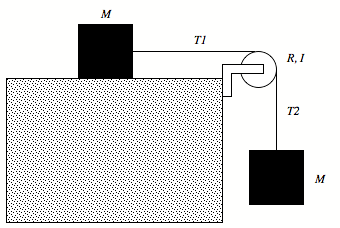
a) What is the angular acceleration a of the pulley?
b) What is the linear acceleration a of the two blocks?
c) What are the tensions T1 and T2 in the upper and lower sections of the strings?
Express all your answers in terms of M, R, I, q, t, and g.
Problem 12 (25 points) Answer in Exam Booklet 1
The system shown in the Figure below is in equilibrium. The mass of the block hanging from the end of the strut S is M, and the mass of the strut itself is m. The density of the strut S is homogeneous.
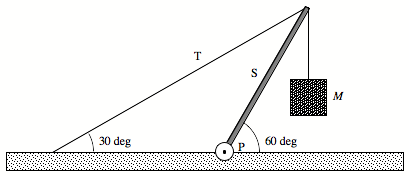
a) Find the tension T in the cable.
b) Find the horizontal and vertical force components exerted on the strut by the pivot P.
Express all your answers in terms of m, M, and g.
Problem 13 (25 points) Answer in Exam Booklet 2