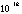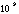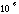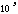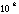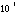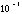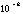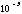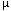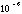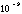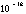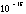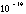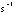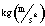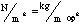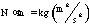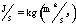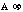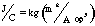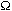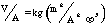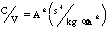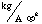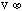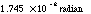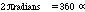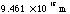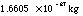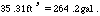APPENDIX A
The International System of Units
The International System of Units(SI), uses a single basic unit
for each physical quantity, and multiples and fractions of this
unit are formed by adding a prefix. For example, the SI unit for
length is the meter (m). The millimeter (mm), centimeter (cm),
and kilometer(km) are formed by adding the prefixes milli- (m),
centi- (c), and kilo- (k) to meter. The same prefixes are used
for all physical quantities. The prefixes and their symbols are
listed in Table A.1.
The following rules should be observed when using SI symbols of
units:
- Do not put a period after a symbol. Therefore, 7 km. is incorrect,
but 7 km is correct.
- Do not put s at the end of any symbol. Therefore, 7kms is
incorrect, but 7 km is correct.
- The symbol for a unit is a lowercase letter except when the
unit is derived from a proper name(i.e. Newton, Pascal, Joule
etc.). Thus, the symbol for the meter is m, whereas the
symbol for the Newton is N. (An exception is the symbol
for L for liter.)
- A symbol with the prefix is treated as a new unit which can
be raised to a power without using brackets. Thus, the notation
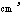 means
means 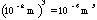 , and not
, and not 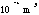 .
.
Table A.1- SI Prefixes
| Prefix | Symbol
| Value |
| tera- | T |
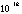 |
| giga- | G |
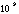 |
| mega- | M |
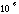 |
| kilo- | k |
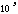 |
| hecto- | h |
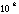 |
| deca- | da |
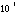 |
| deci- | d |
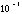 |
| centi- | c |
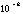 |
| milli- | m |
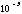 |
| micro- | 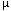 |
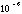 |
| nano- | n |
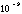 |
| pico- | p |
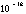 |
| femto- | f |
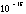 |
| atto- | a |
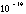 |
Table A.2- Common SI Units
Fundamental Units
| Quantity | Name of Unit
| Symbol of Unit |
| Length | Meter | m
|
| Mass | Kilogram | kg
|
| Time | Second | s
|
| Temperature | Kelvin | K
|
| Electric Current | Ampere |
A |
Derived Units
| Quantity | Name of Unit
| Symbol of Unit | Unit(with Fundamental Units)
|
| Frequency | Hertz
| Hz | 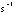
|
| Force | Newton
| N | 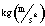
|
| Pressure | Pascal
| Pa | 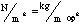
|
| Energy | Joule
| J | 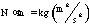
|
| Power | Watt
| W | 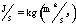
|
| Electric charge | Coulomb
| C | 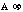
|
| Electric potential | Volt
| V | 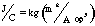
|
| Electric resistance | Ohm
| 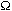 |
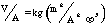 |
| Electric capacitance | Farad
| F | 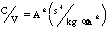 |
| Magnetic filed | Tesla
| T | 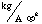 |
| Magnetic flux | Weber
| W | 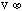 |
Table A.3- Conversion Factors
| Unit | Conversion Units
|
| 1 degree | 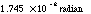
|
| 1 revolution | 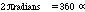
|
| 1 meter | 3.281ft=39.37in.
|
| 1 light year | 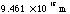
|
| 1 kilogram | 2.205lb=35.27oz
|
| 1 atomic mass unit | 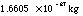
|
| 1 slug | 14.59kg |
| 1 cubic meter | 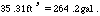
|
| 1 joule | 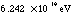
|
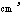 means
means 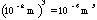 , and not
, and not 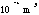 .
.
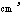 means
means 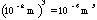 , and not
, and not 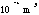 .
.